Using RFID in Warehousing: Is It Worth It?
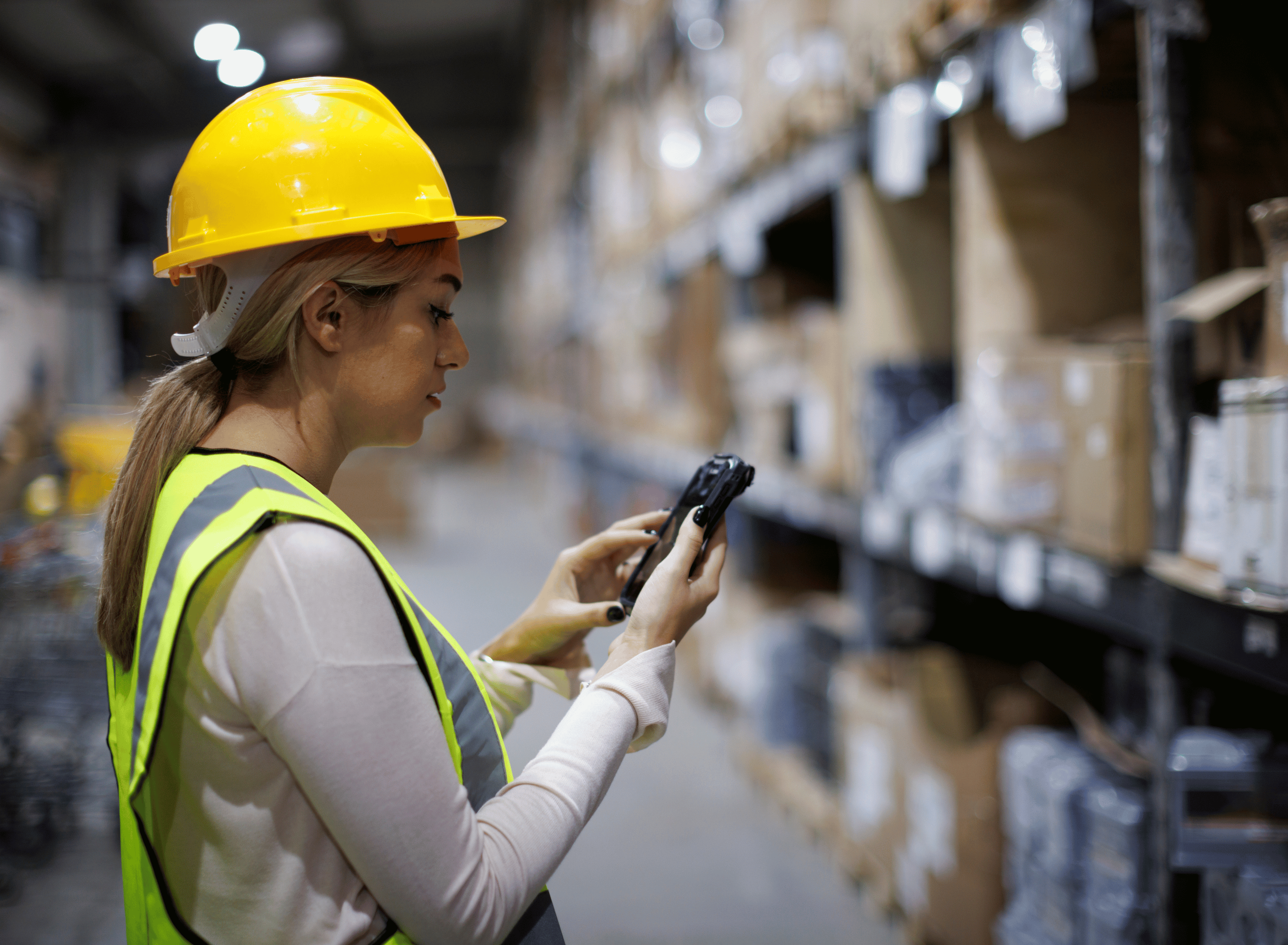


What Is RFID?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. These tags contain electronically stored information and can be read from several feet away—without requiring a direct line of sight.
In warehousing, RFID is often used to:
Track inventory movement in real-time
Reduce manual scanning and paperwork
Improve inventory accuracy
Enhance security and traceability
Warehousing Without RFID
Most warehouses today still rely on barcodes, manual entry, and human labor to manage inventory. While this can be effective with strong processes, it comes with challenges:
Lower upfront cost
Easier to implement with existing systems
Familiar to most workers
Cons:
Prone to human error (misscans, data entry mistakes)
Requires line-of-sight for barcode scans
Time-consuming inventory counts
Delays in tracking and reporting
Warehousing With RFID
Implementing RFID brings automation and visibility into warehouse operations.
Pros:
Real-time tracking of goods
Hands-free scanning—no need for line-of-sight
Faster inventory audits (can scan hundreds of items in seconds)
Improved accuracy (fewer errors and discrepancies)
Reduced labor costs over time
When Does RFID Make Sense?
RFID might not be the right fit for every warehouse. It shines in environments where:
Inventory moves fast and frequently
Mistakes are costly
You need real-time data visibility
There’s a need to reduce headcount or reallocate labor
Industries like retail, pharmaceuticals, automotive, and electronics tend to benefit the most from RFID due to the high volume and sensitivity of goods.